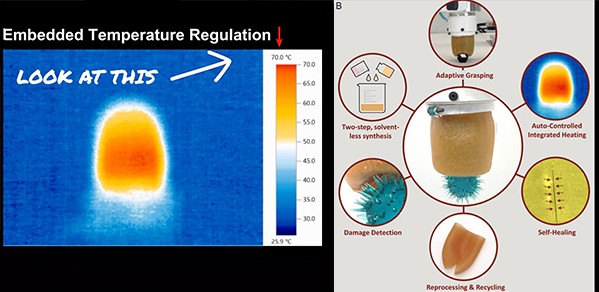
Researchers have developed a self-healing robotic gripper for use in soft robotics that is adaptable, recyclable and resilient to damage, thanks to heat-assisted autonomous healing.
Where damage is too large to heal, we have designed a gripper with high recycling potential, one that can be completely melted down, reprocessed and reshaped into a new gripper – presenting a sustainable option for universal grippers and soft robotics in general in the future.
Professor Fumiya Iida
A self-healing elastomer forms the flexible and deformable membrane of the gripper. Developed by researchers at the University of Cambridge and Vrije Universiteit Brussel, the elastomer – a special class of polymer with unique properties such as elasticity and toughness – is able to self-heal from macroscopic damages, including scratches and punctures sustained from direct contact with sharp objects or surfaces.
A pressure sensor acts as the damage detection early warning system. Meanwhile, autonomous integrated heating achieves rapid healing in approximately nine minutes at the desired temperature of 70°C.
Unlike other universal robotic grippers, this proposed self-healing universal gripper can be fully reprocessed and recycled – something that is in contrast to the traditional silicones currently used in soft robotic grippers, which offer poor recyclability and a limited lifetime. The results are reported in the journal Advanced Intelligent Systems.
Soft and flexible materials are typically used for the fabrication of soft robots as they are shock-absorbent and can protect the robot from mechanical impact. These materials enable soft universal grippers to conform to, grasp and handle a wide range of different and irregular shaped objects.
The researchers found the self-healing universal gripper to be capable of grasping a range of objects reliably in a pick-and-place task including pliers, marker pens, rolls of tape and screwdrivers. This is due to the gripper’s design, which is based on particle jamming. Highly conductive steel balls enclosed within the self-healing membrane help to maximise heat transfer to aid in the autonomous healing process. The steel balls can also be reused in a new gripper or can be reprocessed through melting.
“The self-healing polymer that we have used for our soft gripper has excellent mechanical strength, an adaptive grasp and is resilient to damage,” said Professor Fumiya Iida. “Where damage is too large to heal, we have designed a gripper with high recycling potential, one that can be completely melted down, reprocessed and reshaped into a new gripper – presenting a sustainable option for universal grippers and soft robotics in general in the future.”
Experimental results showed that there was no closure or sealing of the damaged polymer at temperatures below 70°C.
The research team investigated the healing performance of the polymer membrane in four ways:
- By cutting the surface with a scalpel to mimic damage caused by sharp objects or jagged edge.
- Piercing the polymer with a needle to replicate damage posed by thorny objects such as broken glass and spiky twigs.
- Cutting and tearing to inflict fatal damages to the gripper that are likely to occur before leading to catastrophic failure of the gripper.
Microscopic analysis of a polymer sample, which was healed from being cut in two and fractured under force in a tensile test, showed that a new fracture had occurred at a location that differed from the original scar. According to the researchers, this finding demonstrates three things: firstly, the successful and complete healing of the detached two parts; secondly, the full recovery of the polymer’s mechanical properties; and thirdly, confirmation of there being no weak point created at the location of the original scar.
Huijiang Wang, co-lead author and Marie Sklodowska-Curie Early Stage Researcher in Soft Robotics, said: “Preserving the high mechanical performance and stability of polymers alongside rapid healing at ambient temperature (either by heat or light) has proven to be a challenge for the self-healing materials community. However, with our gripper, the entire self-healing process – damage detection, reorientation (turning the gripper upside down into its ‘healing position’ to increase contact between the steel balls and the integrated heater) and temperature regulation – is performed autonomously, without any need for human intervention, creating a system that is good as new and capable of returning to its tasks.”
Reference:
Huijiang Wang et al. ‘Self-Regulated Self-Healing Robotic Gripper for Resilient and Adaptive Grasping’. Advanced Intelligent Systems (2023). DOI: 10.1002/aisy.202300223

