A wearable ‘smart’ choker for speech recognition has the potential to redefine the field of silent speech interface (SSI), say researchers – thanks to embedded ultrasensitive textile strain sensor technology.
The synergy of our sensor design and neural network optimisation sets a new standard in wearable silent speech communication technologies, offering a comfortable smart choker with groundbreaking potential.
Dr Luigi G. Occhipinti
Where verbal communication is hindered, such as in locations with lots of background noise or where an individual has an existing speech impairment, SSI systems are a cutting-edge solution, enabling verbal communication without vocalisation. As such, it is a type of electronic lip-reading using human-computer interaction.
In new research, led by the University of Cambridge, an overlying structured graphene layer is applied to an integrated textile strain sensor for robust speech recognition performance, even in noisy environments.
Worn around the neck, the smart choker captures micromovements in the throat, which are then picked up by the strain sensor as an electrical signal and fed into brain-inspired computer software models for processing and speech recognition. It can pick up even silently mouthed words and broadcast it, which could help someone who is unable to speak following laryngeal surgery, for example.
The smart choker’s unique structure features ordered thorough cracks on graphene-coated textiles. The structured graphene layer significantly enhances the sensitivity of the strain sensor. It can dynamically respond to throat micromovements, enabling the capture of information-rich speech signals. These signals are then processed through a computationally efficient neural network, with a record accuracy of 95.25% in speech decoding.
The results, reported in the journal npj Flexible Electronics, offer a promising, non-invasive solution for practical, wearable SSI systems, paving the way for seamless, natural silent communication in diverse settings.
The proposed SSI system is robust and able to decode a wide range of words, while swiftly adapting to new users and vocabularies. The technology was recently showcased as a live demonstration at the IEEE Biosensors 2024 conference, attracting the attention of 180 plus participants to the event.
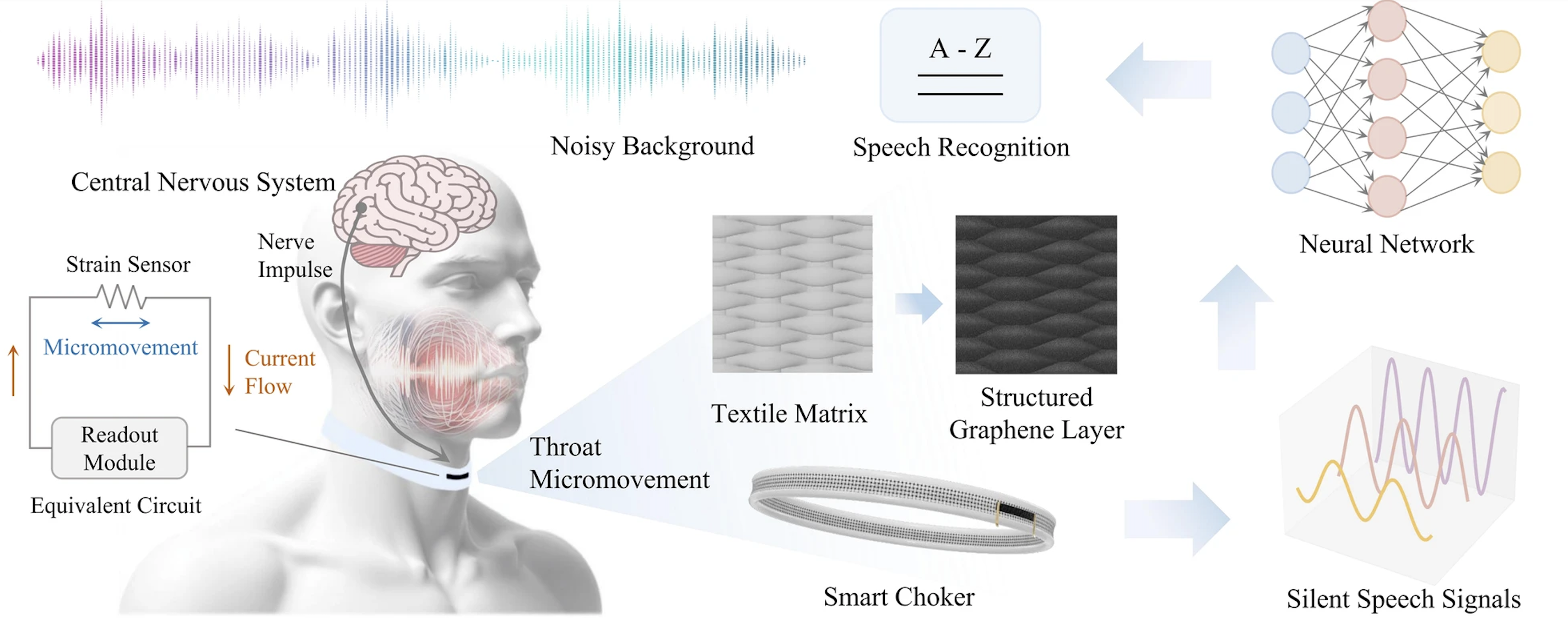
An overview of the wearable SSI, featuring an ultrasensitive strain sensor and a neural network for efficient speech recognition.
The research was led by Dr Luigi G. Occhipinti, Director of Research in Smart Electronics, Biosystems and AI, and Head of the Occhipinti Group in the Electrical Engineering Division at the Department of Engineering and the Cambridge Graphene Centre.
Dr Occhipinti said: “Our user-friendly smart choker demonstrates a remarkable ability to efficiently perform in real-world scenarios with users of different genders, geographical, and ethnic backgrounds, across new and potentially ambiguous words of varying lengths and familiarity, and at varying reading speeds.
“Our SSI system operates with high precision and computational efficiency in distinguishing the speech of different users against different types of noise, caused by sensor imperfections, the external environment, and/or from the users’ own body movements while wearing the device.
“Furthermore, the fabrication method of our ultrasensitive textile strain sensor technology is biocompatible, simple, low cost, and scalable. It is also adaptable to prolonged use and can withstand more than 10,000 stretching-releasing cycles while maintaining stable and reliable electrical functionality.
“Put simply, the synergy of our sensor design and neural network optimisation sets a new standard in wearable silent speech communication technologies, offering a comfortable smart choker with groundbreaking potential.”
Reference:
Chenyu Tang, Muzi Xu, Wentian Yi, Luigi Giuseppe Occhipinti, et al. ‘Ultrasensitive textile strain sensors redefine wearable silent speech interfaces with high machine learning efficiency’. npj Flexible Electronics (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41528-024-00315-1

